Chest pain is an expression often used by patients to describe their discomfort in the chest. It is more than just a feeling; it is more than just discomfort; it actually refers to whenever any of these three things are present or happen: pain, discomfort, or something that feels like something else. Chest pain can be caused by problems with various cardiac structures and valves that are related to the heart itself, but it is more usually caused by something else.
This article is not medical advice and you should see it for educational purposes only. It is a general overview.
What is Chest Pain?

Chest pain is a medical condition that usually refers to sharp, stabbing, dull, tight, or aching sensations in the breastbone area and around it. The real definition of chest pain is a symptom that is usually a result of a cardiac problem, but it could also be a result of other structural or even functional problems in the chest region. Chest pain can therefore be considered to be any type of discomfort felt in the region between the neck and abdomen which could have been caused by the organs present in the chest area. The heart, lungs, and esophagus are some important structures situated within this region, and therefore chest pain may arise due to any disorder associated with these structures.
Reasons for Chest Pain
Angina Pectoris
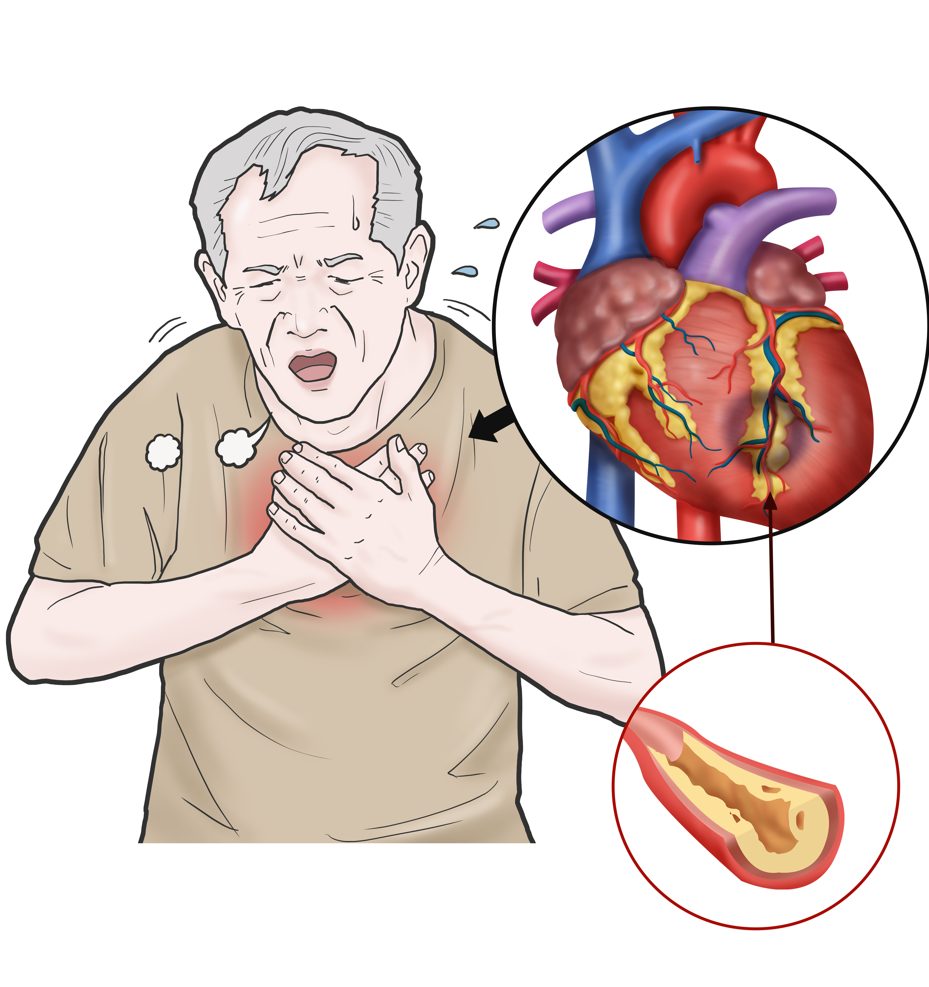
Angina pectoris is usually described as a recurrent pain or discomfort which may be persistent or even interrupted by periods of relief. This type of chest pain happens due to insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle, and it is due to some coronary artery disorder, more commonly by narrowing of the arteries. This is not a serious condition and usually doesn’t require any further treatment as it heals itself over time, but medicines such as aspirin and nitrates can be used for relieving pain and discomfort associated with it.
Cardiomyopathy with Hypertrophy (HCM)
Cardiomyopathy with hypertrophy, commonly known as HCM, is a type of heart disorder that results in enlargement of the heart chambers, the organelles, and the muscles. This enlargement results in over-stretching of the muscle tissue causing it to weaken. It has been found that almost 75% of cases are hereditary, which means it could have been passed on by our parents.
This disorder can also affect other organs within the chest region, such as the lungs and this condition is very serious because it affects blood vessels. Other conditions associated with cardiomyopathy, such as pericardial effusion, can lead to complications such as shortness of breath and fluid accumulation around the cardiac structures. The symptoms of this disorder usually include dyspnea, chest pain, and palpitations.
Asthma

Asthma is a condition that refers to a disorder of the respiratory system. The symptoms associated with this condition include shortness of breath, coughing, and increased secretions from the airways. These symptoms could be triggered by viral or bacterial infections, but in most cases, they occur due to allergies such as dust and pollens.
This is not a serious condition and therefore requires no further treatment, but it can be managed by the use of an inhaler such as Ventolin, which works by relaxing the muscles surrounding the airways, thus opening them up and allowing free flow of air through them.
Strains and Injuries to the Muscles

Strains and injuries to the muscles is a very common cause of chest pain. Injuries or even strains to the muscles could be caused due to accidents, especially due to falls, but they could also occur in daily activities such as lifting heavy weights or even pulling a heavy car door closed. Chest pain can be caused by problems with various cardiac structures and valves that are associated to the heart, but it is more usually caused by something else. A doctor may advise some analgesics or even anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen for reducing stiffness and discomfort in case of injuries.
Other causes of chest pain include diseases like infections, tumors, and stress. Sometimes when medication is prescribed for one of these diseases, it can also cause chest pain in conjunction with another disease which makes this occurrence very rare, but it still needs further evaluation to determine its cause.
If you experience pain in your upper back while walking, it may be due to muscle strain or injury. To alleviate the discomfort, you can try simple stretches, gentle massages, or apply heat and cold packs. You can also seek professional help, such as physical therapy or chiropractic treatment. For more information about upper back pain, check out Upper Back Pain When Walking: Definition, Symptoms And ….
Walking And Chest Pain

Walking is considered light physical activity, which also includes most gardening. Most people can perform light physical activities with no difficulty after an extended time of not exercising or if they do not continue at the same level of activity. This level of activity does not cause excessive fatigue, weakness, or shortness of breath for most people. However, it is possible that walking or other light physical activities can cause chest pain in some people because their bodies are continuing to move despite the pain.
The amount of time that has passed since an activity or exercise can affect how quickly pain returns. After you exercise, the muscles of your body begin to relax after you stop moving. If there is an injury, the impact on your muscles may not be realized for several days or weeks after the activity. Changes in posture (such as hunched over) might also create discomfort in the muscles of the chest wall.
Short-distance Walking
The normal motions of walking can cause pain if they are performed improperly; however, it is also possible to experience pain while walking. Two factors may accelerate the return of pain after walking: breathing difficulties and posture.
During short-distance walking, you often stand upright with your feet firmly planted on the ground. If you are breathing too deeply (hyperventilation) or not deeply enough (hypoventilation), your rib cage does not expand all the way, causing pain in the chest wall muscles that support your ribs. A cough, sneeze, or laugh can release trapped air within the chest cavity, causing discomfort in some people who are hyperventilating when they breathe in deeply after a cough or sneeze.
When you walk, the muscles and joints of your body change position several times per second. When this motion of the body parts of the ribs, hips, and lower back occurs on a regular basis, or if they change position more dramatically on a regular basis (e.g., when you walk on uneven ground), your body may experience pain due to these repeated changes in position.
If you experience pain in the chest when you walk, the first step is to determine if the pain is caused by breathing or by your movements. This can help determine how quickly you will recover from any underlying illness that is causing the problem. If the pain is caused by breathing, there are a number of things you can do for recovery:
Do you experience chest pain while walking short distances? This could be a sign of an underlying medical condition. It is important to understand how far you can walk in a day to determine your physical limitations. Check out this article on how far you can walk in a single day to learn more about your body’s capabilities.
Long-distance Walking and Chest Pain

When walking long distances, you may experience pain in the chest wall after walking longer distances. If you are breathing deeply or if your pace is not continuous, you can experience pain because of improper breathing. Your body is not getting the oxygen it needs, causing pain to develop due to insufficient oxygen reaching your muscles.
You might also experience pain because of poor technique when changing your breathing rate, causing one breath cycle to last too long or too short. This could be caused by hunching over or sitting up straight during walking. Poor posture can also increase the amount of pressure on the chest wall muscles.
Some people with a history of heart disease might experience pain when walking long distances; when you walk long distances, your heart rate increases to keep up with the demands on the body. This increase in your heart rate may cause chest pain, especially if you have a history of heart disease. In this case, the pain is not felt in the chest wall but rather in the area of the neck and shoulders.
See also: Chest pain while running
Walking after Eating
Being hungry can cause chest pain because you are not getting the food that your body needs to function properly. However, you might also experience chest pain due to digestion while walking. The motion of digesting food pushes fluids and gases through your system and into the colon (large intestine). If this motion is not sufficient, it can push fluids and gas into areas of the body where they do not belong (such as the chest area), causing discomfort.
Walking should not be painful after eating; however, it may cause increased belching, bloating, or other abdominal symptoms that could be painful. These symptoms are normal after eating. It is possible that your abdomen is not fully empty after eating, causing pressure on the area below the ribs.
Walking after Severe Operations
Severe operations can cause chest pain because they damage or irritate nerves in your body. These nerves send messages to the brain about how much pain you are experiencing. If the nerves have been damaged, it is possible that they do not send a strong enough message to your brain about the level of pain that you are experiencing.
If this happens, you might mistake a moderate amount of pain for a severe level of pain. In this case, it is recommended that you stay in bed for several days after these operations, where you can receive proper care from a healthcare professional rather than moving around and possibly causing more damage to your body.
Walking after undergoing severe operations can be a challenge, especially if you experience chest pain. It is important to take precautions and wear comfortable shoes that provide proper arch support like the ones discussed in What Is Arch Support and Why You Should Wear Them?. Wearing the right shoes can help reduce the impact on your feet and legs, which can reduce the risk of developing blood clots or exacerbating existing medical conditions.
When Should You See a Doctor?

Many different conditions might cause chest pain. You should see your doctor if it’s severe or lasts more than a few minutes, especially if you are healthy and have never had chest pain before.
If you are unable to get in to see the doctor, there are other options for treatment. Some of these treatments include over-the-counter medicines that ease the discomfort while waiting for an appointment with your doctor or just time to wait till your symptoms go away. If this doesn’t work, then you may need to come in for further treatment, depending on how severe your injury is.
Options for Treating Chest Pain
There are several options in dealing with chest pain. The doctor may suggest over-the-counter medicines. If they don’t work, you may need to see a doctor for more treatment. You can also try to do athletic stretches or breathing exercises until you are able to see your doctor. This could be very helpful if the cause of the chest pain is really muscle-related. Your doctor will then recommend treatment that can range from taking medicine or even surgery depending upon how serious the condition is.
The two most common options for treating chest pain are medicine and exercise. A doctor may give you Benadryl or some other kind of antihistamine to make your chest feel better. The doctor will also use any of the above-mentioned methods if they feel that you will be able to relieve the pain on your own with these options. Another common choice is pain relievers, again depending on how severe your condition is. These are also some of the options for treating chest pain that is available without medical attention.
Prevention
First and foremost, always seek medical care immediately when you experience chest pain. There is no reason to wait before seeing a doctor if it’s severe or lasts longer than a few minutes, and it may even be dangerous. It’s also important to see your doctor about chest pain that is accompanied by shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, or any other changes in behavior. Many people with these symptoms will have no idea what they are due to and will go undiagnosed for many years.
One type of exercise that can help prevent chest pain is breathing exercises. Breathing exercises can be very helpful when coupled with any other therapies that you need in order to reduce your symptoms and prevent future problems from occurring. You can also take medicines such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin. These can be very helpful in preventing chest pain in the future.
You may want to consider taking a drug called a beta-blocker, which reduces the electrical impulses in your heart and can decrease chest pain in a number of cases. However, it’s important to understand that this medication is not a cure for heart disease, and it will not prevent heart disease from developing in the future. For this reason, it should be taken only when there is no chance of other, more serious health issues developing or when other medications have been ineffective.
To prevent hip pain from standing for long periods of time, check out these 4 causes & prevention tips. It is essential to wear comfortable shoes and take short breaks to stretch your legs and hips.
Is it Possible to Tell If Chest Pain Is Caused by a Heart Condition?
Many different disorders can result in chest pain. You should see your doctor if it’s severe or lasts more than a few minutes, especially if you are healthy and have never had chest pain before. Many cases of chest pain are acute and will pass on their own without any treatment.
However, it’s important to pay attention to what the cause of the symptoms is so that you can act quickly for treatment for any other areas that may be affected. If your symptoms are severe enough to not improve or linger more than a few minutes, the first thing you should do is seek medical attention right once. Seek medical care right away if you are experiencing chest pain that has any of these symptoms:
Pain that gets worse when you take a breath in. Chest pain accompanied by wheezing or difficulty breathing is usually caused by pulmonary disease or fluid in your lungs. This can be life-threatening and must be treated promptly. If the cause of this pain is an injury to the chest, the pain may subside on its own after a few days. But if there are no other more serious effects, treatment will not be needed until the injury has healed.
Chest discomfort that worsens with breathing out. Chest pain accompanied by shortness of breath is often related to heart disease or blood vessels that run through the chest. This can be very serious, especially if you are suffering from chest pain that worsens when you take a deep breath or are suffering from shortness of breath when at rest. You should get medical attention even if the chest pain only occurs when you are exercising since this indicates possible heart disease.
How Can You Know If Your Chest Pain Is Muscular or Not?
Chest pain that is associated with both pain and shortness of breath, as well as that occurs when you bend your arms or chest forward or breathe out, is likely to be due to a heart condition. If you experience this kind of pain and it goes away on its own after a few minutes, then you probably don’t need any further medical treatment. But if your chest pain persists for longer than a few minutes or if it gets worse on its own without any reason, then the following may help you determine the cause.
One way to determine the cause is by looking at your medical history. If there are any underlying conditions that may be causing the symptoms, they should be listed in the chart below. This will help you assess the severity of each case.
A second way to determine if your symptoms are due to musculoskeletal issues is by having a physical examination. The doctor should assess your condition and perform some palpation tests to determine whether there are any areas in need of treatment or therapy. If there are muscle-related symptoms that can be treated by exercise, then it will be much easier to rule out other health conditions that may be causing the symptoms. If there are no muscle-related symptoms, then you should be able to figure out the cause of your pain with this information.
Related: Pulled Chest Muscle
FAQs
Why does my chest hurt when I walk?
It’s important to note that chest pain is not synonymous with the sensation of pain in the heart or chest. Chest pain can be caused by many factors, including cardiac, musculoskeletal, neurological, paraspinal, and even psychological conditions.
The most common cause of chest pain is a heart attack. When your heart gets enlarged or ruptures, the walls of your heart become thick, and this can cause chest pains. Other causes of chest pain are more common, including back pain, referred pain, nausea/vomiting, indigestion, and constipation.
Chest pain is often accompanied by shortness of breath or dyspnea. This may be caused by more than one cause. Causes of chest pain include cardiac conditions (heart attacks, angina), muscle strain or spasm, narrowing of some blood vessels in the heart (coronary artery disease), cancer, asthma and other lung diseases, gallstones in the gallbladder, or liver disease (including cirrhosis), anxiety or anxiety disorders (such as a panic attack). Chest discomfort is sometimes associated with osteoarthritis.
How do you know if chest pain is muscular or heart-related?
This is an important question because people with chest pain often don’t know whether it’s muscular or heart-related. You may feel fine one minute and experience chest pain the next moment. The discomfort can last for several seconds, minutes, or even hours. Chest pain can be mild to very severe in intensity, depending on the cause. Chest pain may last until the underlying cause is corrected, it may come and go for a while, or it may be continuous for many years.
Chest pain can also be referred from other organs in your body to your chest wall, making the condition worse than it really is. For example, if you have gallstones in your gallbladder, it may cause you to feel worse when you walk. This is because the pressure on your abdomen when walking causes the gallbladder to contract (squeeze) and aggravates the situation even further.
Does walking help chest pain?
This is a difficult question to answer, as there is no single type of exercise that has been proven to reduce chest pain. One study found that walking can be beneficial if it is done at a brisk pace and is combined with therapy for chronic pain. Another study showed that walking could also be helpful in cases where there are no heart or chest pain symptoms present.
Another study found that sitting at a desk for hours per day can contribute to shortness of breath and muscle tension, which can contribute to the development of chest problems. These may not usually cause you any problems because your nervous system compensates for them by increasing the number of deep breaths you take per minute. However, the changes that occur in your respiratory system can be too much for some people, who may then develop chest pain.
Therefore, it is generally recommended that you begin taking short walks every hour or so to reduce your risk of developing chest pain associated with sitting at a desk for long periods of time. It will also help you avoid various health issues that can arise from sitting at a desk for too long.
How do I know if my chest pain is serious?
Chest pain can be mild to very severe in intensity, depending on the cause. Chest pain may last until the underlying cause is corrected, it may come and go for a while, or it may be continuous for many years.” If you are experiencing chest pain that lasts more than 10 minutes, please seek medical attention immediately. You should consider this if you have chest pain that radiates into your neck or arms, if you have trouble breathing or if you feel like you are going to faint. In addition, there are several other reasons why chest pain is a serious condition and should be treated immediately.
Being overweight can cause rib pain due to the excess pressure on the chest, in both standing and walking positions. So, if you experience chest pain while walking and you are overweight, it could be a sign that you need to start losing weight. Check out these weight-burning exercises to help you with your weight loss journey.
When should you go to the hospital for chest pain?
The most important thing to remember about chest pain is that if it does not go away on its own, you should seek medical attention right away. It’s also important to seek medical attention if your chest pain is accompanied by other symptoms, such as shortness of breath or emotional changes. You should do this regardless of your age, regardless of whether you have heart disease, and regardless of whether the chest pain is related to exercise or stress.
Go to the hospital immediately if your chest pain is severe or if you are unable to breathe. You should also go to the hospital immediately if you believe that you have a heart attack. The fastest way to determine whether you have a heart attack is by using an electrocardiogram (EKG). If this test comes back with any abnormalities, then it’s important that you ask for an immediate stress test, as these can give the most accurate results in determining whether there’s a serious problem. If these tests are done, and they come back normal, then it means that you do not have a heart attack.
If you are still not sure whether or not you have a heart attack, then you should ask for another test called an exercise stress test. This test can determine if your heart muscle is working properly by measuring how well it can pump blood throughout your body. If the results of these tests come back normal, then it doesn’t necessarily mean that no heart problem exists, but it does mean that your risk of having a serious heart problem is very low. Hopefully, this will be enough to convince you to continue to take everything else into consideration and see your doctor for further evaluation and possible treatment.
